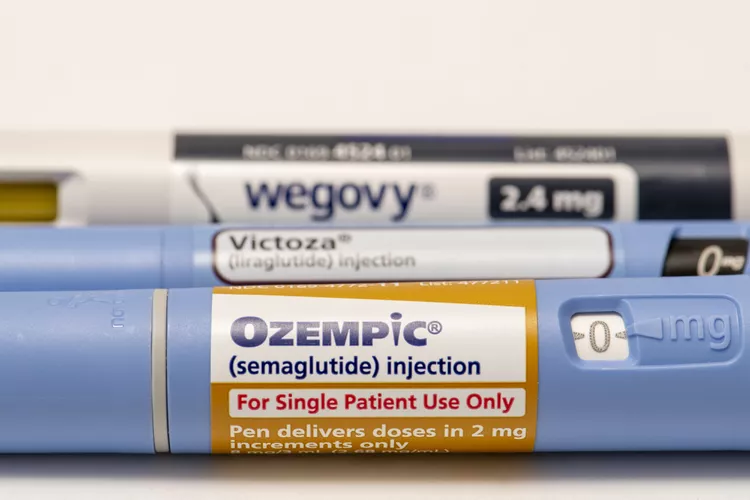
Peptides for weight loss are injectables called glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 agonists).These medicines help break down glucose (sugar) and reduce your appetite, which can help you control your calorie intake so you can lose weight.
How Do Peptides Help You Lose Weight?
Peptides are parts of proteins that transmit signals throughout your body. Naturally occurring peptides your body produces include hormones, such as insulin, ghrelin, leptin, and glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1). These peptides regulate your appetite, blood sugar, and energy usage.
Synthetic peptides like glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 agonists) are injectable medications that are made in a lab. They were initially developed for type 2 diabetes. These medicines mimic the effects of GLP-1, helping you lose weight by:
- Decreasing glucose (sugar) levels
- Suppressing your appetite
- Increasing your metabolism
- Helping you burn fat
Which Peptide Is Best for Weight Loss?
The use of GLP-1 agonists for weight loss has skyrocketed as they’ve gained traction on social media and among celebrities. However, the best peptides for weight loss depend on several factors. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved several peptide medications for weight management. The following GLP-1 agonists may promote weight loss:
- Ozempic, Wegovy (semaglutide): The FDA approved Ozempic for type 2 diabetes, but it may be taken off-label (meaning it has not been FDA-approved) for weight management Wegovy, on the other hand, is FDA-approved for long-term weight management. Ozempic and Wegovy are taken as once-weekly injections at any time of day, with or without food. Wegovy is approved for adults who are obese (having a body mass index or BMI greater than 30) or overweight (having a BMI greater than 27) plus have other conditions like diabetes or high blood pressure. It’s also approved for children over age 12 with a BMI in the 95th percentile. Studies have shown that weight loss from Wegovy plateaus at around 60 weeks.
- Victoza, Saxenda (liraglutide): Victoza is FDA-approved for controlling blood sugar in people with type 2 diabetes. Saxenda is FDA-approved for weight loss and weight management. Saxenda is given as a daily injection. It can be given at any time of the day, regardless of food. Saxenda is approved for adults with a BMI greater than 30 or those with a BMI greater than 27, plus other conditions like diabetes or high blood pressure. Children over 12 with a BMI greater than 30 and weighing over 60 kilograms can also take it. If you haven’t lost weight after 16 weeks on Saxenda, you’ll probably need to switch medications. Effects may slow down after this point.
- Mounjaro, Zepbound (tirzepatide): This medicine is considered dual-acting. It acts at the body’s GLP-1 and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) receptors. Mounjaro is FDA-approved for type 2 diabetes. It’s taken off-label for weight loss. Zepbound is FDA-approved for obesity. Zepbound is given as a weekly injection. It can be given at any time of the day, with or without food.
Other injectable peptides may help build muscle mass or reduce body fat but are not associated with weight loss per se. These peptides include:
- Egrifta (tesamorelin): This medicine helps the body release growth hormone. The FDA approved it to decrease abdominal fat in people living with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV).
- Geref (sermorelin): This medicine increases the amount of human growth hormone in the body. It’s unlikely to cause weight loss but may increase lean muscle mass. However, this medication has been discontinued and is no longer available in the US.
- CJC-1295: A synthetic peptide that mimics growth hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH). It is used as a performance-enhancing drug and has been banned in dietary supplements in the United States. According to the FDA, CJC-1295 may cause significant adverse reactions.
- Ipamorelin: Another performance-enhancing drug that stimulates the release of growth hormone. Ipamorelin can cause serious adverse reactions, including death. It has not been approved by the FDA for human consumption.
Do Peptides for Weight Loss Really Work?
Peptides like GLP-1 agonists have proved effective for weight loss. How well they work depends on several factors, including the following:
- Whether you have type 2 diabetes: People with diabetes tend to lose less weight with GLP-1 agonists compared to people who don’t have diabetes.
- Diet and exercise: Combining peptides with diet changes and increased physical activity is most effective for weight loss.17 Expect weight loss to be less dramatic if you use peptides without these lifestyle interventions.
- The specific medicine you use: Long-acting weekly injections seem to be more effective than daily ones.
Keep in mind that not everyone who uses peptides will lose weight. Studies show that only one in three people with type 2 diabetes who use peptides without also changing their diet or exercise will lose more than 5% of their body weight.
Will You Need to Take Them for the Rest of Your Life?
The short answer is, possibly, yes. Many people who achieve weight loss by taking peptides may need to stick with their therapy to maintain their weight.
It may be common to regain weight after stopping medication. For instance, a clinical trial showed that people who stopped taking Wegovy regained about two-thirds of the weight they’d lost in one year.
Reaching a weight-loss plateau typically means your body’s metabolism has adapted, not that your medicine has stopped working.
Maintaining a healthy weight is a great accomplishment. Research shows that losing even 5% of one’s body weight can lower blood pressure and cholesterol levels and improve overall heart health.
How Much Weight Can You Expect to Lose?
The amount of weight you can expect to lose on peptides varies based on personal factors like diet, amount of exercise, and other health conditions you have.
As with many weight loss methods and medications, there’s no easy way to predict how well you will respond to peptides for weight loss or exactly how much weight you’ll lose. However, data from clinical trials suggests the following:
- People with diabetes who take a GLP-1 peptide in addition to diet and exercise changes can expect to lose 4% to 6% of their body weight. Someone who weighs 250 pounds, for example, is likely to lose 10 or 15 pounds.
- People with diabetes who take a GLP-1 peptide without diet and exercise modifications will lose less weight, usually around 3% or 4% of their body weight.
- People without diabetes who take one of these peptides in addition to diet and exercise changes will typically lose more weight. Typical weight loss in this group can be between 6% and 17% of body weight. So, someone without diabetes who weighs 250 pounds is likely to lose 15 to 42 pounds.
Studies show that Zepbound is the most effective specific weight-loss medication, followed by Wegovy and Saxenda.